Practical Frontend Interview Questionnaire for Junior Engineers
✅ Web Development Basics
Would give a basic understanding of candidate's overall web dev concepts & knowledge
Concept of
modulesIdea of
Code Bundling, why needed,webpackconceptsTranspilationProcess, the need for transpilers -BabelTouch up around
CSR, SSR, SSG
✅ JavaScript Language
👉 1. How JS is executed?
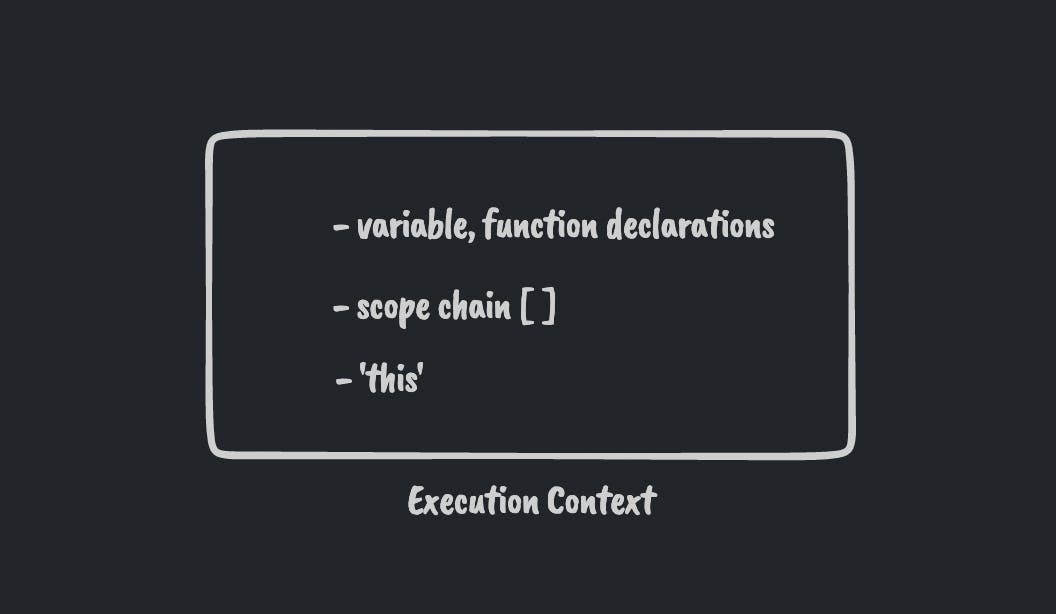
Covers: language understanding, execution context, hoisting, scope, scope chain
Execution context2-pass execution process - code parsing(memory allocation) & execution
Is JS interpreted or compiled? Share some language behaviour insights to support the answer.
HOISTINGenters the chat... 👻Lexical Scope & Scope Chaincan be asked (optional)
//Hoisting output based question
var a = 1;
function b() {
a = 10;
return;
function a() {}
}
b();
console.log(a);
👉 2. Closures
Laymann's terms - We say that there is a closure when a function reads or writes a variable that is declared outside of it's scope.
- Do you see a closure in the below snippet?
let cars = ['Brezza', 'Bolero', 'Nexon'];
let query = 'B';
let filteredCars = cars.filter(function(car) {
return car.startsWith(query);
});
//observed a closure?? 👀
Concept of closure
Use cases - Where have you observed closures?
Examples
Does the JS engine maintain all closure variables in memory or only the variables that are used?
👉 3. this keyword/ call /bind /apply
Covers: this, call(thisValue, a1, a2...), bind(), apply(this, [a1, a2...]), different function invocation types
thisis the context of a function invocation (a.k.a. execution).
//1. output??
const numbers = {
numberA: 5,
numberB: 10,
sum: function() {
function calculate() {
return this.numberA + this.numberB;
}
return calculate();
}
};
numbers.sum();
//2. fix it to log the expected results
//[hint to the candidate]
//check how the calculate is invoked, give hints regarding where the this is pointing
👉 4. arrow function
- Difference b/w regular function and arrow function
//1. output??
function Period (hours, minutes) {
this.hours = hours;
this.minutes = minutes;
}
Period.prototype.format = () => {
return this.hours + ' hours and ' + this.minutes + ' minutes';
};
const walkPeriod = new Period(2, 30);
walkPeriod.format();
//2. fix it
//[hint to the candidate]
//arrow fn takes this from the enclosing context where it is defined
👉 6. Promise
Executepromise code,consumeusingthen,catch,finally

Question 1 - Output
//output??
let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
resolve(1);
setTimeout(() => resolve(2), 1000);
});
promise.then(alert);
Answer
Question 2 - The built-in function setTimeout uses callbacks. Create a promise-based alternative.
function delay(ms) {
// your code
}
delay(3000).then(() => alert('runs after 3 seconds'));
Answer
Question 3 - Order Output
//1. output
console.log("a");
setTimeout(() => console.log("d"), 0);
new Promise((resolve, reject ) => console.log("c"));
console.log("b");
//2. Explain with event loop
Answer
👉 6. Event Propagation
Covers: event propagation - capture, target, bubble, delegation, event object
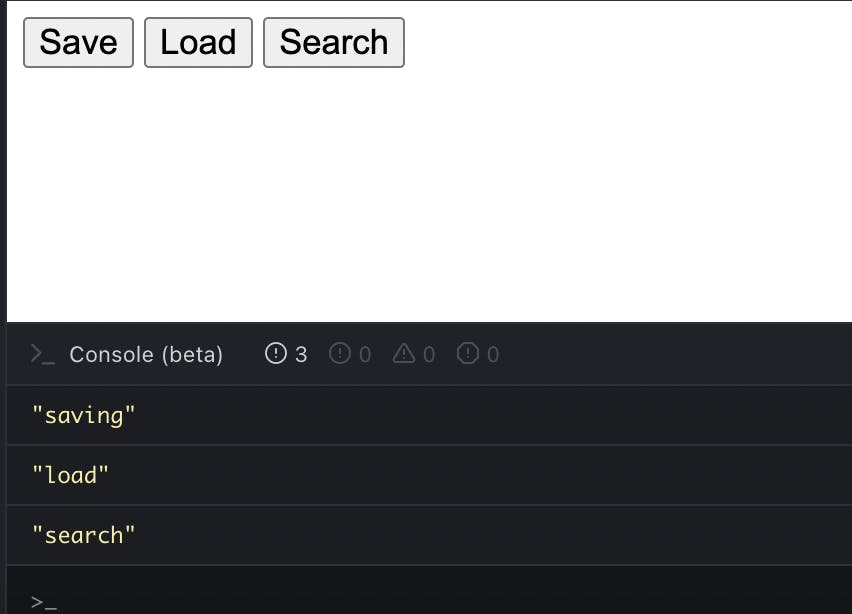
Start with a coding statement -
3 buttons in the UI
on click of save click -- > log "saving"
on click of load --> log "load"
on click of search --> log "search"
What is event propagation - capture, target, bubble
delegation
default phase? - bubble, but configurable with
addEventListenerthird bool arg
✅ React
How React works, Reconciliation
Difference between React and ReactDOM


